

The DPO7000SX ATI Performance Oscilloscope is an amazing instrument, with the ability to capture up to 70 GHz signals with the lowest noise and highest fidelity of any oscilloscope on the market today. But what takes it from being a mere product to a complete test and measurement solution are the more than 50 software option packages that automate compliance testing for important standards or give deep insight for troubleshooting design.
For this post, I thought it would be interesting to look at Option ST14G for the DPO7000SX that provides trigger and decoding features for greater insight when analyzing 8b/10b encoded serial data streams. It enables users to simultaneously view waveforms, character, and low-level protocol activity, simplifying validation of link-level communications and isolation of data-dependent faults.
Engineers implementing serial data interfaces are initially faced with debugging and validating designs for compliance with physical-layer specifications. At this stage, signal integrity and timing stability are key issues. Much of this validation and debug is done using repeating test patterns in conjunction with analysis tools such as DPOJET Jitter and Eye Analysis Software.
After ensuring physical-layer compliance, serial signals change from test patterns to 8b/10b coded traffic and system-level issues become the focus of debugging. As system operation is brought online, problems may be discovered in the physical-layer/link-layer domain. For example, a serial link may pass physical-layer testing and exhibit high-quality electrical signaling. However, faulty transmission logic or signal corruption due to data-dependent crosstalk or power plane bounce can produce incorrect symbols on a seemingly good link. Many of these effects are more efficiently discovered at a character, primitive, or higher protocol level even though their root cause may be in the physical domain.
Option ST14G provides correlated views of physical-layer signaling and link-layer traffic to efficiently isolate and resolve data-dependent faults such as these. In addition, all DPO70000SX models with Option ST14G can trigger in real time on 8b/10b character sequences or 8b/10b coding errors. The combination of Option ST14G and DPOJET gives you a complete solution for debugging, characterizing, and compliance testing systems employing high-speed serial interfaces.
Option ST14G also extends our Pinpoint trigger features to include a hardware trigger solution for 8b/10b encoded serial data up to 14.1 Gbps as shown below. With this capability, you can trigger conditionally on up to 16 consecutive 8b/10b characters specified. Binary trigger patterns are automatically created to recognize either running disparity or you can require a single form. This high-level approach enables greater efficiency and fewer errors when specifying trigger conditions.

Trigger on 8b/10b encoded serial data streams up to 14.1 Gbps
Characters can also be edited independently to create one- to sixteen-character trigger sequences as shown in the screen capture below. You can work in the familiar context of an interface standard using native formats rather than interpreting wave shapes or specifying 1s and 0s. Control characters are specified using Kxx.y format. Data characters are specified using Dxx.y format or by entering their binary value. Trigger conditions are easily correlated with data displays using this common labeling scheme.

With Option ST14G, you can trigger on any control character, data character or symbol. You can set positive or negative disparity or both as well as character of disparity error. You can also trigger on specific patterns up to 16 characters long.
The instrument also responds to character or running disparity errors to provide an efficient means of isolating corrupted traffic. The trigger behaves just like other Pinpoint trigger types in that it continuously monitors and immediately responds to incoming data. In other words, triggering is a real-time function rather than a postprocessing operation. In practice, this makes it possible to trigger on a defined fault condition rather than capturing an arbitrary window of data and then searching to see if it contains an instance of an error. These trigger features provide a unique toolset for isolating faults or navigating in time based on reference events in an 8b/10b encoded stream.
Let’s look at some additional capabilities Option ST14G offers for analyzing your 8b/10b encoded streams:
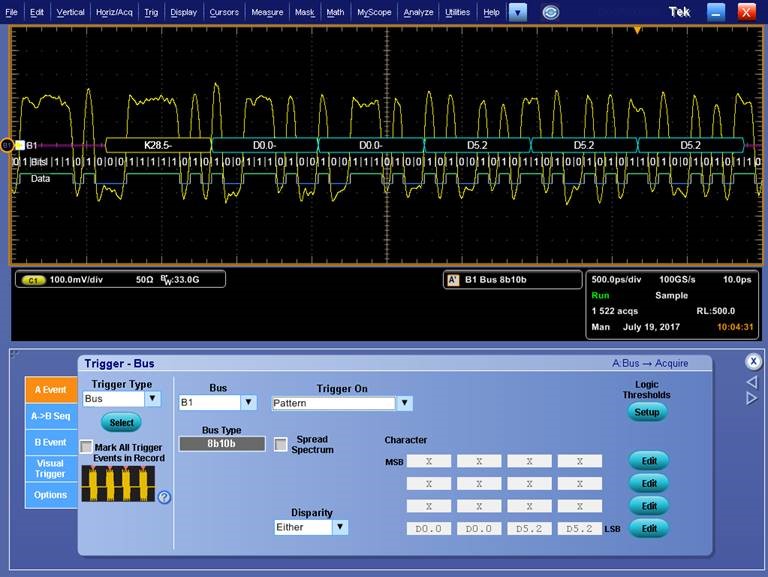
Use the pattern trigger to find specific packets such as TS1 or TS2 ordered sets.

Specify and trigger on patterns up to 16 characters (160 bits).

Quickly discover and find disparity errors and invalid characters by triggering on them directly.

Quickly find problems within long waveform records using the bus decode results table.


Trigger reliably even in the presence of spread spectrum clocking (SSC).


