Contact us
Call us at
Available 6:00 AM – 5:00 PM (PST) Business Days
Download
Download Manuals, Datasheets, Software and more:
Feedback
Arbitrary Function Generators
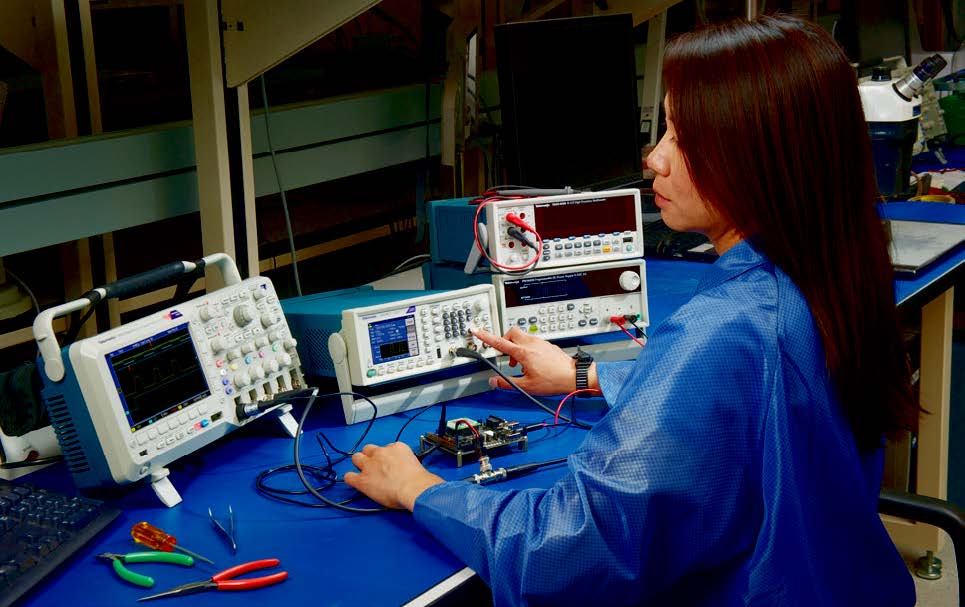
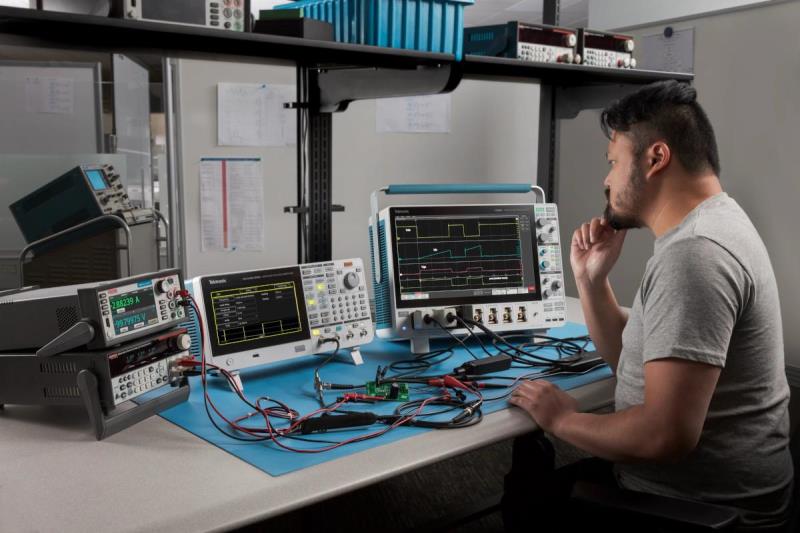
Today's designs are often complex, demanding a variety of stimulus signals during test. Tektronix function generators are best-in-class instruments that deliver uncompromised frequency agility and ensure signals are accurately reproduced every time.
With pre-loaded standard waveforms, arbitrary waveform capability, and signal impairment options, Tektronix function generators support a wide range of applications and provide an economical solution for applications that don’t require the advanced capabilities of an arbitrary waveform generator.
Find the right arbitrary function generator for your application or explore all Tektronix signal generators.
Also on this page
Compare Tektronix Arbitrary Function Generators
| Compare | Model | Analog Channels | Sample Rate | Bandwidth | Vertical Resolution | Record Length | Output Frequency Range | Base Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
1 - 2 |
250 MS/s - 2 GS/s |
25 MHz - 250 MHz |
14-bit |
16 MSa/ch |
25 MHz - 250 MHz |
US $3,050
|
|
|
|
2 |
125 MS/s - 300 MS/s |
25 MHz - 60 MHz |
14-bit |
8k points - 1M points |
25 MHz - 60 MHz |
US $1,230
|
|
|
|
1 |
250 MS/s |
20 MHz |
14-bit |
128k points |
20 MHz |
US $2,710
|
Product series comparison

|

|

|
|
| AFG31000 Arbitrary Function Generator | AFG1000 Arbitrary/Function Generator | AFG2000 Arbitrary / Function Generator |
How to choose an arbitrary function generator
Though there are a number of factors to consider when choosing the right arbitrary function generator for your bench, here are a few of the most important considerations.
| Consideration | Description |
|---|---|
| Sample rate | This affects the frequency and fidelity of the main output signal. The sampling frequency must be more than twice that of the highest spectral frequency component of the generated signal to ensure accurate signal reproduction. |
| Bandwidth | The analog bandwidth of a signal generator’s output circuitry must be sufficient to handle the maximum frequency that its sample rate will support. In other words, there must be enough bandwidth to pass the highest frequencies and transition times that can be clocked out of the memory without degrading the signal characteristics. |
| Record length | This determines the maximum number of samples that can be stored and plays an important role in signal fidelity because it determines how many points of data can be stored to define a waveform. Particularly in the case of complex waveforms, memory depth is critical to reproducing signal details accurately. |
| Output frequency range | Perhaps one of the most important considerations—and often the biggest driver of price—is the frequency range. It’s essential to choose a function generator that can operate in a frequency range that supports your tests. |
| Noise and jitter | These two characteristics are very closely related and are essentially undesired distortions of the signal, which you want to keep as low as possible. |
| Number of channels | Depending on the application needs, a single output may be sufficient. But for IQ modulation for instance, two outputs are mandatory. |
| User interface | A large, modern touchscreen with responsive feedback has become a key factor in labs where test time is essential. |
Resources
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is a function generator used for?

A function generator is a piece of electronic test instrument used to generate and deliver standard waveforms, typically sine and square waves, to a device under test. It can be used to test a design or confirm that a piece of electronic equipment is working as intended.
What’s the difference between a function generator and a signal generator?
A signal generator is any device that creates electronic signals. A vector signal generator specializes in creating RF signals with analog and digital modulation schemes in formats such as QAM, QPSK, FSK, BPSK, and OFDM.
A function generator is a specialized piece of test equipment that has a preset list of waveforms or patterns that it can play. Function generators are known for their ability to rapidly switch from one frequency to another and are a more economical option than other more advanced waveform generators.
How do function generators work?

A function generator connects to a device under test (DUT) via test leads and creates voltage waveforms at a desired frequency to the DUT. Using the instrument’s front panel, the operator can change the parameters of a waveform, such as how fast it’s played, the amplitude and offset, or add basic distortion or modulation.
What is the difference between a function generator and an arbitrary waveform generator (AWG)?
A function generator primarily produces standard waveforms like sine, square, and triangle waves, while an arbitrary waveform generator (AWG) can create more complex and custom waveforms based on user input. AWGs are often used for advanced applications like high-speed signal testing.
What types of waveforms can a function generator produce?
Function generators can produce a wide range of waveforms, including sine waves for AC circuit testing, square waves for digital signal testing, triangle waves for waveform analysis, and arbitrary waveforms for custom signal generation.
Can I synchronize multiple function generators?
Yes, many function generators allow synchronization through various methods such as external triggers or synchronization inputs/outputs. This is particularly useful for generating complex waveforms or multi-channel setups.