What is Autoranging?
Autoranging digital multimeters are electronic tools used to measure a variety of electrical parameters, including voltage, current, resistance, ohms, power rating, and more. As the name suggests, autoranging equipment can automatically select the appropriate measurement range for the parameter being measured.
Autoranging DC power supplies work by analyzing the input voltage (or other input signal) before determining the appropriate output voltage (or output signal). By adjusting the range to match the input signal, autoranging DMMs ensure that readings are accurate and reliable, even for rapidly changing or fluctuating signals.
These devices measure the amps, volts, or ac/dc current to determine which range will best support your testing protocols. They can also measure capacitance, DC voltage, impedance, and a wide array of other variables to test an electronic product. With the basics of “What is autoranging?” now covered, it’s time to explore the benefits of these AC/DC voltage testing tools.
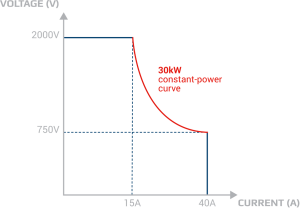
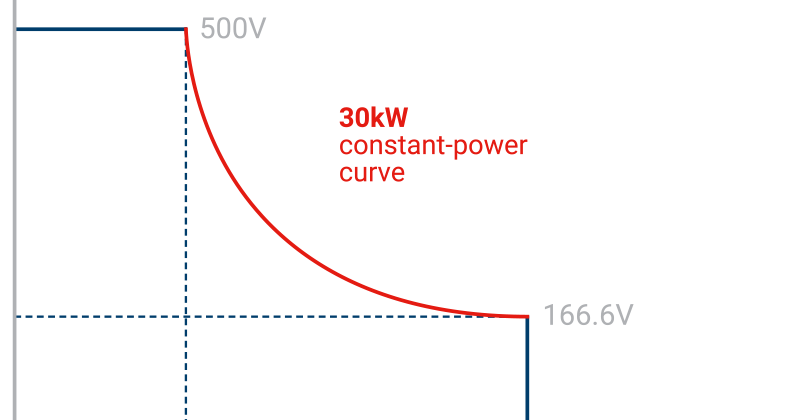
Autoranging supplies, on the other hand, are not so constrained. They automatically supply higher output current at lower voltages, and when current outputs are modest, can supply a higher output voltage than traditional supplies. This feature gives autoranging power supplies extra range and more flexible performance than traditional supplies.
Benefits of Autoranging
Benchtop DC power supplies equipped with autoranging capabilities provide a wide range of benefits over traditional electrical testers, which require manual adjustments. By investing in autoranging equipment, you can unlock advantages such as the following:
Improved Accuracy
The latest generation of DMMs has an LCD display that clearly relays the selected testing ranges. This information helps your research team document precisely which ranges are used to test diodes, capacitors, and other components. As a result, they can avoid manually selecting testing ranges and instead focus solely on their work.
Autoranging also eliminates the risk of over-voltage or under-voltage conditions, ensuring the reliable operation of connected devices. This leads to improved confidence in your evaluation protocols and more impactful research.
Ease of Use
Autoranging DMMs eliminate the need for manual adjustments of voltage settings, providing your team with added convenience. With modern power supplies, your team can simply plug in the device and trust that it will automatically give the correct voltage. Whether your staff has lots of experience using DMMs or is relatively new to the evaluating process, they can effortlessly perform reliable experiments.
Versatility
Power supplies from EA offer versatility by adapting to different load conditions without manual intervention. As a result, our equipment can support a wide array of applications, from field operations to high-voltage uses. Fill multiple equipment needs with these modern devices and ensure your staff has the tools they need to thrive.
How Autoranging Works
The autoranging process is relatively straightforward. The devices are equipped with advanced circuitry to detect the voltage requirements of the load and adjust the output voltage accordingly. This process involves voltage sensing circuits that measure the voltage level of the load and range selection circuits that determine the appropriate range to deliver.
By continuously monitoring the load and adjusting the output voltage, autoranging power supplies ensure optimal performance and efficiency. If the input values change, the equipment will adjust the outputs in response.
Fixed-Range Power Supplies vs. Autoranging
Fixed-range power supplies offer a limited number of voltage settings. More importantly, each of these settings features a fixed range, which means testers cannot select a voltage option outside of one of these pre-set thresholds. As such, they are limited in their ability to test equipment and structure experiments.
Conversely, autoranging options offer a wide array of voltage settings, making them suitable for a broader mix of applications. Additionally, they eliminate the need for manual adjustments, which reduces the risk of human error and offers a simpler operation.
Applications of Autoranging
There are two common use cases for DMMs and power supplies with autoranging capabilities: testing and measurement and portable devices.
Testing and Measurement
DMMs’ primary function is to test and measure the performance of electronic devices. Every industry that deals in electronics, including the automotive, consumer goods, and commercial technology sectors, relies on autoranging solutions to create better products. To do this, they use a combination of diagnostic tools and power supplies.
There are three main types of tools, known as true RMS (root mean square) or TRMS devices, that can measure AC current or AC voltage:
- TRMS digital multimeters (clamp meters)
- Oscilloscope
- Average-responding digital multimeters
Digital clamp meters and average-responding DMMs are more commonly used than oscilloscopes. True RMS devices are the most accurate and are used to measure a wide range of circuits, including those found in:
- Electronic ballasts
- Converters
- HVAC systems
- Variable-speed motor drives
The bi-directional power supply is another commonly used tool. Researchers use it to test leads and other aspects of electronic components. These evaluations are employed to set warranty terms and ensure that products function as designed before being sold to consumers.
Portable Devices
Aside from diagnostics and research purposes, autoranging technology also plays a vital role in the function of portable devices. Sophisticated equipment like smartphones, laptops, tablets, and wearable tech rely on various voltages to function properly.
Autorangers dynamically adjust the output voltage to match the requirements of the load. This allows them to ensure optimal performance and efficiency in portable applications.
Whether you are engaging in research and product performance measurement or are designing a portable piece of equipment, it’s vital that you have access to high-quality autoranging tools. With that in mind, the following explores how these devices compare to manual ranging and outlines key considerations for choosing an equipment supplier.
Autoranging vs. Manual Ranging
Before you select a power supply or piece of testing equipment, it’s important to understand the nuances of autoranging and manual ranging. Here’s a look at the pros and cons of each approach.
The Good and Bad of Autoranging
DMMs that can automatically set and adjust the voltage range offer some huge advantages over old-school manual technology. For starters, these devices provide enhanced accuracy, as they control for human error and precisely match the input load’s requirements.
Additionally, autoranging solutions provide significant convenience, as your team doesn’t have to manually select voltage settings. This will save time and give them the opportunity to focus on their work.
Most importantly, DMMs that adjust outputs independently are not locked into preset voltage options. They can meet the needs of more applications and fill key equipment needs in your workspace.
The primary downside associated with autoranging equipment is that they typically have a higher initial cost compared to their manual counterparts. After all, they are more sophisticated and require complex circuitry to function. However, the best options can fill multiple roles within your business and provide long-term efficiency gains. Cumulatively, these advantages will offset any initial upfront cost differences.
The other potential drawback is that autorangers can be more complicated to maintain and prepare. Fortunately, you can mitigate this concern by sourcing your power supplies from a reputable manufacturer that offers a good warranty and high-quality support. Providers like EA ensure that you get the most out of your investment by standing behind our equipment.
Pros and Cons of Manual Solutions
It’s also important to consider the good and bad of manual power supplies. On the positive side, manual ranging power supplies typically have a lower initial cost than their more sophisticated counterparts, making them more budget-friendly.
Additionally, these devices are easy to use as long as your team knows the basics of setting testing ranges based on input voltages. The devices offer great reliability as well, thanks in large part to their simplicity. However, if your staff’s experiments require a broader range of settings, manual equipment might not adequately meet their needs.
The major concern with manual ranging power supplies is their potential for human error. Your team will have to manually adjust voltage settings. Choosing the wrong threshold can skew experiment results or damage the product under analysis. Seemingly small mistakes can create downstream issues, such as reliability problems and added project costs.
Manual-ranging power supplies offer a limited range of voltage options. Therefore, you may need a different device for each use case. If your project calls for frequent voltage adjustments, manual systems may decrease overall efficiency. That’s because your staff will need to pause, run new calculations based on input changes, and make the requisite adjustments.
Despite offering simplicity and cost-effectiveness, manual options are less versatile than their autoranging counterparts. For most organizations, the latter will offer a better return on investment.
Considerations for Choosing Autoranging Power Supplies
Before you choose a solution for your organization, it’s important to consider several important attributes and capabilities, including:
- Voltage Range: Consider the minimum and maximum voltage levels you need and ensure the supply can accommodate them
- Current Capacity: Calculate the maximum draw of your devices and choose a supply that exceeds this value to avoid overloads
- Accuracy: Look for specifications such as voltage and load regulation, which indicate the degree of accuracy that a supply offers
- Efficiency: Higher efficiency power supplies waste less energy and generate less heat
- Protection Features: Look for over-voltage safeguards to prevent your device from damage
- Size and Form Factor: Choose a solution that meets your space constraints
On that last point, consider whether you need something lightweight and portable or prefer a more powerful, rack-mountable device. There aren’t any right or wrong choices. It’s all a matter of finding the solution that best fits your organization’s needs.
Tips for Evaluating Autoranging Features
Most equipment lists numerous features, making it challenging to narrow your search to a few top options. To cut through the noise, focus on some of the capabilities that add the most value, such as voltage sensing.
Supplies with robust voltage sensing mechanisms can accurately detect the requirements of the load and seamlessly switch to the appropriate range. Also, consider the range selection mechanism. Ideally, you want a supply that minimizes switching time while also avoiding voltage overshoot or undershoot.
Perhaps most importantly, you must verify that the equipment you are considering is compatible with your existing devices and systems. By doing so, you can ensure a seamless integration and optimal performance without compatibility mismatches. Finally, get your team involved in the selection process so they can help choose equipment that offers a user-friendly interface.
Source Your Autoranging Equipment
Are you ready to tap into the benefits of autoranging equipment? If so, we invite you to reach out to our sales team.


