How to Choose the Best Oscilloscope to Buy
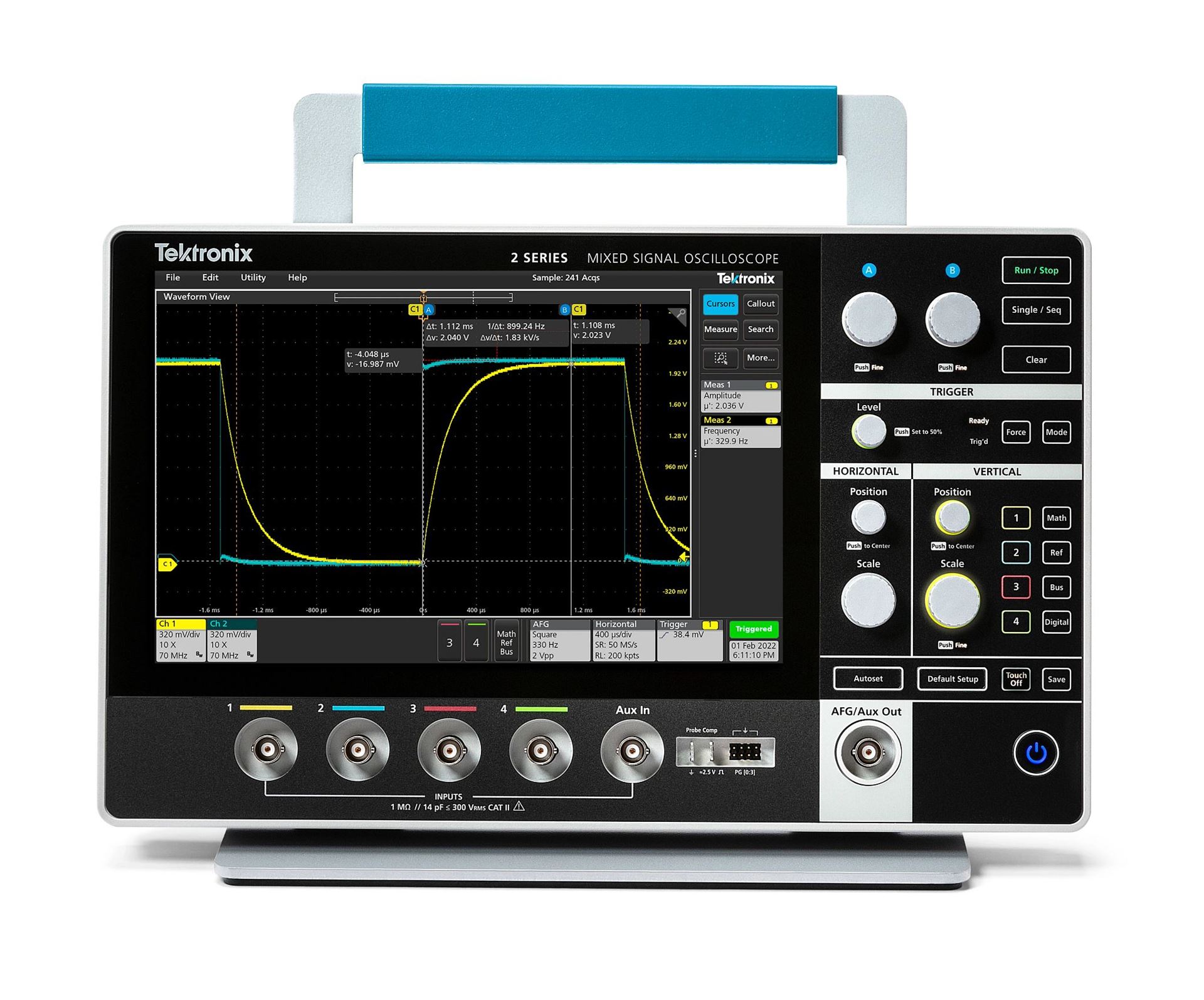
Basic Parameters for Choosing an Oscilloscope
Oscilloscope Bandwidth
Bandwidth is a key spec that determines the highest frequency your oscilloscope can measure accurately. It's a vital consideration affecting both the functionality and cost of the oscilloscope.
The higher the bandwidth, the more accurate the reproduction of your signal, as illustrated with a signal captured at 250 MHz, 1 GHz and 4 GHz bandwidth levels.
How to Calculate Your Bandwidth Needs
When selecting an oscilloscope, a good practice is to use the following formula to ensure you cover the highest frequency component of your signal:

For example, if your highest signal frequency is 20 MHz, you should consider an oscilloscope with a bandwidth of at least 60 MHz.
Oscilloscope Rise Time
Rise time is crucial for digital applications, indicating the scope's ability to track rapid changes in a signal.
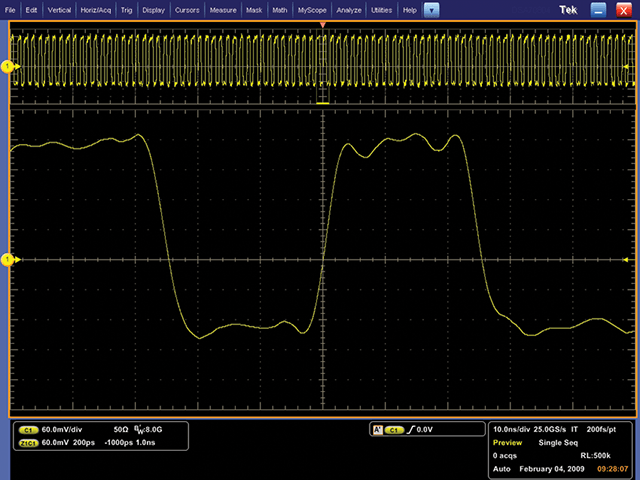
Rise time characterization of a high-speed digital signal.
Calculate How Much Rise Time Your Oscilloscope Needs
The rise time of the oscilloscope should be significantly shorter than the fastest rise time in your signal. Use this formula to find a suitable oscilloscope:
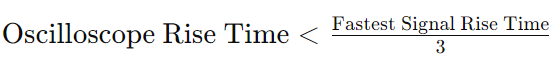
For a signal with a 4 ns rise time, the oscilloscope's rise time should be less than 1.33 ns.
Oscilloscope Sample Rate
The sample rate indicates how frequently the oscilloscope samples the signal, impacting the detail of the waveform captured.
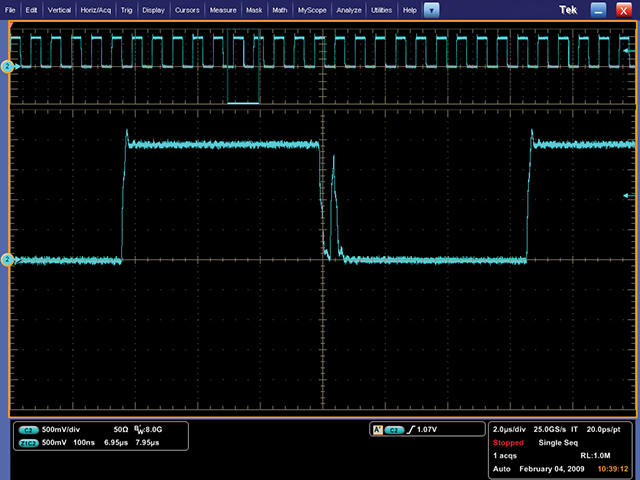
A higher sample rate provides greater signal resolution, ensuring that you'll see intermittent events.
Determine the Right Sample Rate for Your Oscilloscope
To choose an adequate sample rate, use the following guideline:
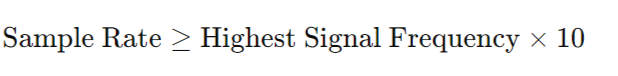
For a signal with a 20 MHz maximum frequency, aim for an oscilloscope with a sample rate of at least 200 MS/s. This ensures a detailed capture of the waveform, facilitating accurate analysis.


