There are several approaches you can take to work remotely with Tektronix oscilloscopes. The available techniques differ somewhat between instruments that run the Windows operating system and instruments that do not. This guide is designed to help you interface with your oscilloscope without needing to physically interact with the instrument after the initial setup. This document applies to most Tektronix oscilloscopes that do not have a PC operating system installed.
Oscilloscopes that run the Windows operating system offer different alternatives for working remotely. The Technical Brief “Working Remotely with Tektronix Oscilloscopes Running the Windows Operating System” offers information on interfacing with Windows oscilloscopes.
This Technical Brief covers:
- Remote operation using an oscilloscope's e*Scope LXI web server
- Offline waveform analysis and remote operation using TekScope PC Software
- File sharing using USB storage devices and network file-sharing
- Programmatic control by writing your own scripts and programs
- Control over USB and related utility applications
This Technical Brief uses examples that represent 4, 5, and 6 Series MSOs. However, many other Tektronix oscilloscopes offer the alternatives described in this document, including 3 Series MDO, TDS3000B, TDS3000C, MSO/DPO2000, MSO/DPO3000, MDO3000, MSO/DPO4000, MDO4000, and more.
The 5 and 6 Series oscilloscopes may be configured to run the Windows operating system with an optional, removable solid-state drive.
Details on remote oscilloscope usage can also be found in Help manuals. Please contact Tektronix technical support if deeper assistance is needed, either through www.tek.com/support or by asking your local Tektronix support contacts.
Working remotely with an instrument often suggests or requires network access between a computer and the oscilloscope – for these situations be sure to consult your IT Department, Cyber Security staff, or Management for guidance or permission.

REMOTE CONTROL USING BUILT-IN WEB SERVER
Many modern Tektronix oscilloscopes feature a built-in webserver called e*Scope. On the 4 Series MSO, 5 Series MSO, and 6 Series MSO, e*Scope is an easy to set up, realtime display and interface that runs on a web browser as if you were at the instrument with a mouse and keyboard. Anyone with the IP Address can simultaneously access and control the oscilloscope.
On many entry-level and previous generation oscilloscopes, e*Scope is a remote User Interface that allows you to quickly see a snapshot of the oscilloscope display and make adjustments to settings and measurements. Examples of these oscilloscopes include TDS3000B, TDS3000C, DPO2000, MSO2000, DPO3000, MSO3000, MDO3000, DPO4000, MSO4000, MDO4000, 3 Series MDO and more.
SETTING UP THE OSCILLOSCOPE
e*Scope requires a network connection between a modern web-browser and an oscilloscope. The web-browser may be running on a computer, smartphone, or other device. The network connection can be a direct connection with an Ethernet cable, a Local Area Network connection with a network switch or router, over a VPN, or via an externally accessible IP Address. You may need your IT Department's assistance or permission to connect the instrument to a network.
When the oscilloscope is connected to a network that you can access, you need to find the oscilloscope's IP Address. This is typically in a Utility or I/O configuration menu.
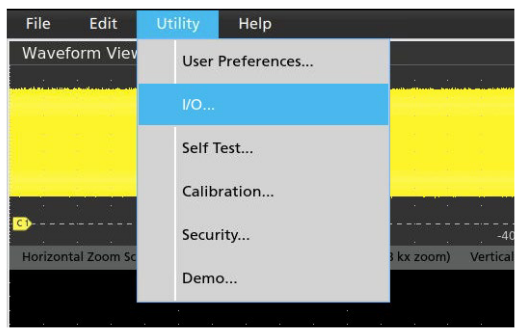
In the I/O settings, you can find an automatically configured IP address or set a static IP address. Make note of the IP address to be ready to enter it into your web-browser's address bar.
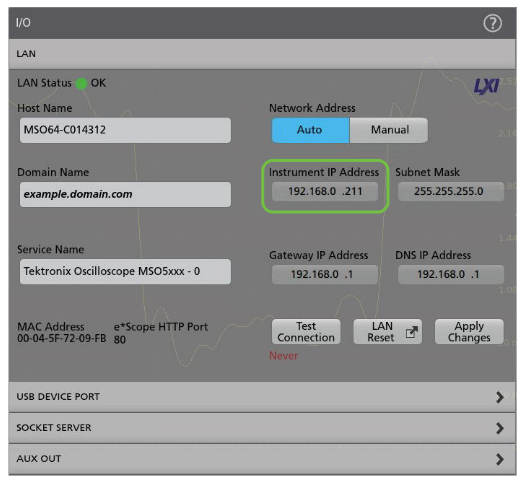
ACCESSING THE OSCILLOSCOPE THROUGH A WEB BROWSER
Enter the oscilloscope's IP Address into the address bar of a web-browser. When you navigate to that IP Address as if it were a website, the oscilloscope will present you with a Home page with several connection and configuration options, including a link to e*Scope. Click the link to e*Scope to connect to the oscilloscope for remote control.
FILE SHARING
No file sharing method is built-in to e*Scope. The File Sharing section of this guide explains a method of mounting network drives that works nicely with most e*Scope instruments.
TROUBLESHOOTING AND SUPPORT
For additional instrument-specific guidance on e*Scope, please refer to the Primary User Manual or Online Help Manual for that oscilloscope model on Tek.com. You can also contact Tektronix technical support through www.tek.com/support or by asking your local Tektronix support contacts.
TEKSCOPE PC WAVEFORM ANALYSIS SOFTWARE AND REMOTE SCOPE DATA ACQUISTION
Tektronix offers a PC-based analysis application called TekScope that can allow you to analyze previously-saved waveforms for free, without connecting to an oscilloscope. You can also connect to one or more oscilloscopes as a paid service to pull real-time data from the remote scopes. You can access this software and see more details at scope.tekcloud.com.
This software allows engineers to collaborate without necessarily having to share physical access to an oscilloscope and provides increased flexibility in each individual's workflows. Consider the following examples of workflows that this software enables:
- One engineer can take data in a lab and send it to several other engineers with this free software installed, and everyone can independently make measurements.
- An engineer can spend one day in an instrumentation lab to collect a large set of data, but the rest of the week at their desk or out-of-office doing analysis.
- As with other remote control options, users with the "MultiScope Analysis" option can connect directly to networked oscilloscopes to adjust instrument settings, collect new data and transfer waveforms all from the TekScope interface to be viewed and analyzed in a centralized user interface.
The TekScope interface duplicates the features and userfriendly interface of 4/5/6 Series MSOs. Any engineers that are familiar with those oscilloscopes will feel right at home with this software, and any unfamiliar users should find the interface easy to pick up.
TekScope supports importing waveforms in a variety of formats from a variety of vendors. Typical oscilloscope measurements, math capabilities, plots, cursors, etc. are available for free, while application-specific analysis features are available as paid services. For a summary of features and options, please see scope.tekcloud.com/#/packages.
FILE SHARING
Every modern Tektronix oscilloscope has the capability to save Waveforms and Setups to internal and external storage. Habitually saving your work can make it easier to collaborate on-the-fly and look back at old projects. Anything from a TDS3000C oscilloscope to a 4 Series MSO to a DPO70000SX can save waveforms to a USB drive, for example. Many oscilloscopes can also be connected as a client to network drives for remote file management.
Most recent non-Windows oscilloscopes, including DPO2000, MSO2000, DPO3000, MSO3000, MDO3000, DPO4000, MSO4000, MDO4000, 3 Series MDO, 4 Series MSO, 5 Series MSO, and 6 Series MSO have a File Utilities system through which you can mount a network drive as well.
SAVING AND RECALLING FILES
Both direct and networked file management options can usually be accessed in the File menu of an oscilloscope. In the following example from a 6 Series MSO, the Recall selection can be used to load waveforms, setups, "sessions" (an all-inone save type) and masks. The Save and Save As selections can be used to store screen captures, waveform data, setups, sessions and generate reports. The File Utilities selection is where you can connect to a network drive or do things like copy and paste, delete, and rename files on the oscilloscope's local memory
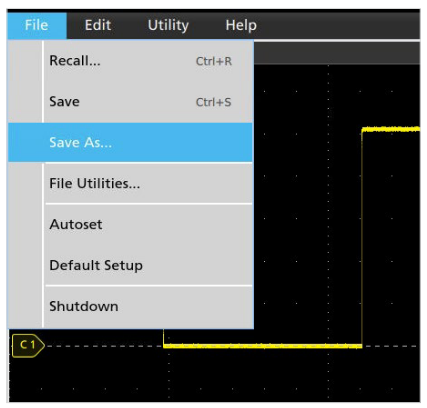
In the Save As menu, the save location can be altered with the "Browse" button. At the very least, the oscilloscope's local memory (in this example, the C drive) will be accessible. If a USB Drive or Network Drive is connected, those locations will also appear as options.
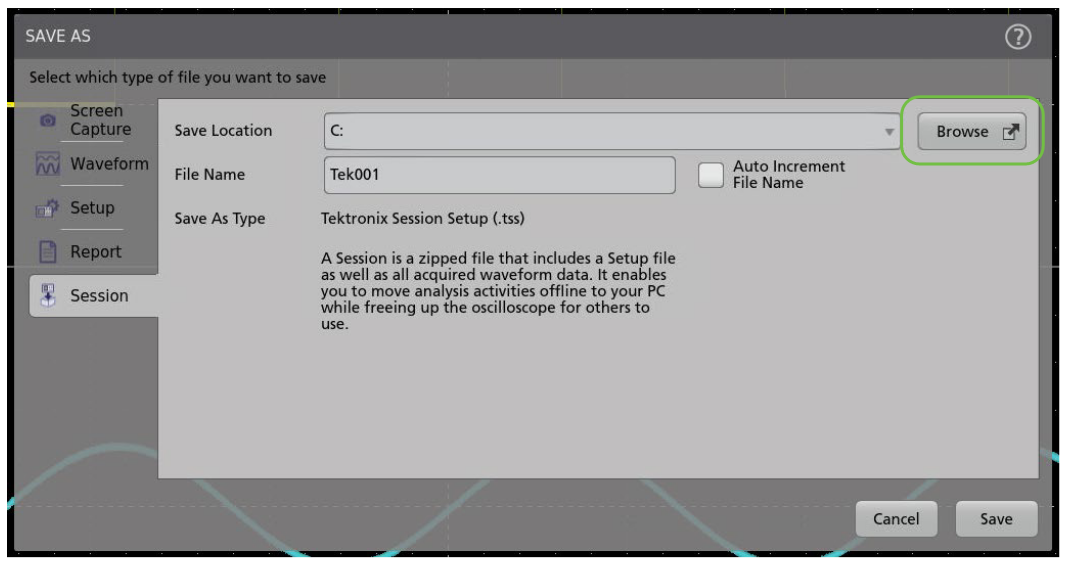
PREPARING A NETWORK DRIVE ON A WINDOWS PC
Connecting to a Network Drive is often simple to configure on the oscilloscope but can sometimes be difficult to configure from a security and networking standpoint. The first step is to make some file, folder or directory accessible from a host server or computer to a network that the oscilloscope is on as well. The next step is to either Mount the network drive on a non-Windows oscilloscope or browse to it through File Explorer on a Windows Oscilloscope.
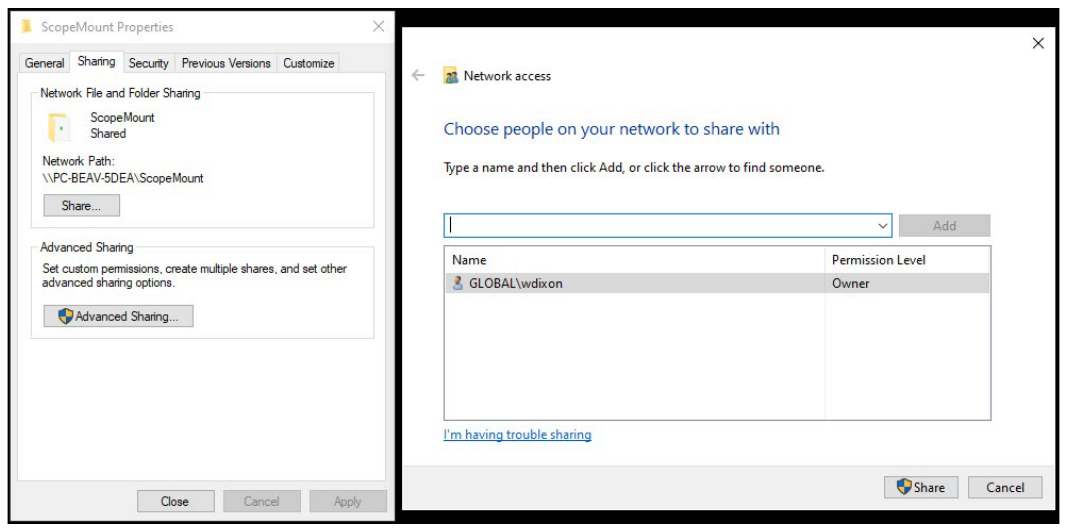
As an example, to share from a Windows 10 PC, you can right click on a folder you wish to make your network drive, go to Properties, and then Sharing. In the new dialog that pops up, called Network Access, the list of Names are the users whose credentials can be used to access this shared folder. In other words, if left as the default, only your username and password can be used to access this new network drive, but you can optionally add more users or open the folder up to everyone on the network.
When user access is configured as you like it, press Share in the Network Access dialog to finally host the network drive. The following image is an example of a simple configuration.
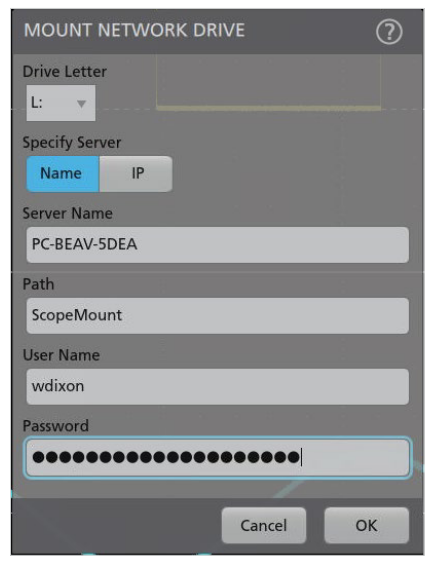
MOUNTING THE NETWORK DRIVE FROM THE OSCILLOSCOPE
To access this folder on a networked non-Windows oscilloscope, you can now go to File Utilities and enter the required fields. The following image shows a typical example of how each field maps to the folder settings in the previous image. An IP Address can be used instead of the server name.
A more detailed walkthrough for this example is available at tek.com/support/faqs/how-do-i-set-network-drive-my-5-series-mso-or-6-series-mso.
PROGRAMMATIC CONTROL
Nearly every Tektronix oscilloscope with an external communication port (e.g. GPIB, USB, Ethernet) can be controlled with remote commands. This is a powerful, flexible and scalable method of remotely controlling your instrument and automating measurements. There is a higher upfront development cost to get up and running when compared with the other methods available to you, but basic scripting is surprisingly easy to accomplish.
Tektronix instruments use SCPI style commands which are industry standard ASCII strings and therefore language-agnostic, which means any language and environment can be used for control. Commonly used languages for this include Python (with PyVISA), MATLAB (with the Instrument Control Toolbox), LabVIEW, and the C-family.
PROGRAMMING RESOURCES
Guides on programmatic control and the variety of remote commands with detailed descriptions can be found in the instrument's Programmer's Manual. You can find this on Tek.com, easily accessible by searching for your model number and filtering by "Manual" and then by “Programmer.”
Examples of scripts can be found around the internet.Tektronix resources include:
- Tektronix online forum at forum.tek.com/viewtopic.php?f=580&t=133570
- Tektronix GitHub at github.com/tektronix.
In addition, the Tektronix Support YouTube channel has a video of getting started from the ground-up for free in Python here:youtube.com/watch?v=W5Brxiwnp5g.
INSTALL A VISA
It is important to be aware of VISA (Virtual Instrument Software Architecture) applications and to have one installed. VISA is an I/O API that is largely industry standard, with many Test and Measurement vendors supplying their own implementation. See mathworks.com/hardware-support/ni-visa-keysight-visatekvisa.html for a few examples. While in general which VISA you use should not matter, it sometimes does, and sometimes installing multiple VISAs can cause conflicts.
Some additional standard protocol specifications that commonly manage I/O on top of VISA are USB-TMC for USB control and VXI-11 for TCP/IP control. Some users choose to use Raw Sockets instead of VXI-11 based control over Ethernet.
CONTROL WITH USB AND UTILITY APPLICATIONS
Many oscilloscopes can be controlled over USB via their USB-B port. While USB control often results in lower throughput and latency than Ethernet-based control methods, USB provides a network-less and convenient connection. Often USB control uses SCPI commands, as discussed in the Programmatic Control section of this guide, with a GUI on top. Three notable examples of applications that support USB connections are TekScope Utility, OpenChoice Desktop, and Keithley KickStart.
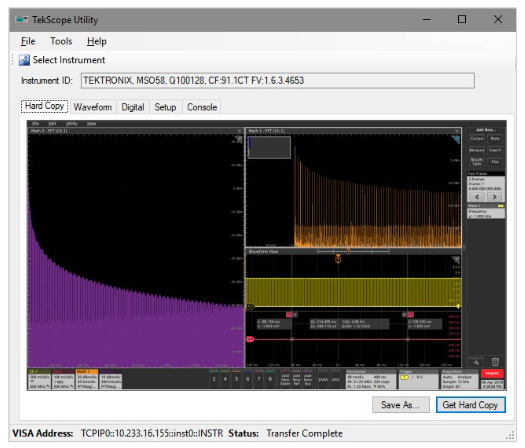
TEKSCOPE UTILITY FREEWARE
TekScope Utility is a free utility application written by a Tektronix engineer with a simple, usable GUI with access to commonly scripted features such as screenshot transfer, measurement logging, action-on-trigger, and waveform data transfer. This utility supports most recent and several older Tektronix oscilloscopes range from entry-level to ultra-high-performance.
TekScope Utility freeware is available at forum.tek.com/viewtopic.php?t=140451.
OPENCHOICE DESKTOP
OpenChoice Desktop is a free official utility application provided by Tektronix that supports the most common simple behaviors like screenshot and waveform transfer on many previous generation oscilloscopes.
OpenChoice Desktop is available at Tektronix Openchoice Desktop Application TDSPCS1 V28.
KEITHLEY KICKSTART
Keithley KickStart is an inexpensive official software that supports a variety of Tektronix and Keithley instruments. Common simple behaviors on oscilloscopes are supported, but KickStart provides many built-in data collection behaviors on Keithley DAQs, SMUs, DMMs, and Power Supplies. Engineers working with Tektronix and Keithley instruments in tandem should consider Kickstart.
Kickstart is available at tek.com/keithley-kickstart.
There are many approaches to controlling and getting data from Tektronix oscilloscope that run the Windows operating systems. The approach you take depends on your application and may also depend on your company's policies.


